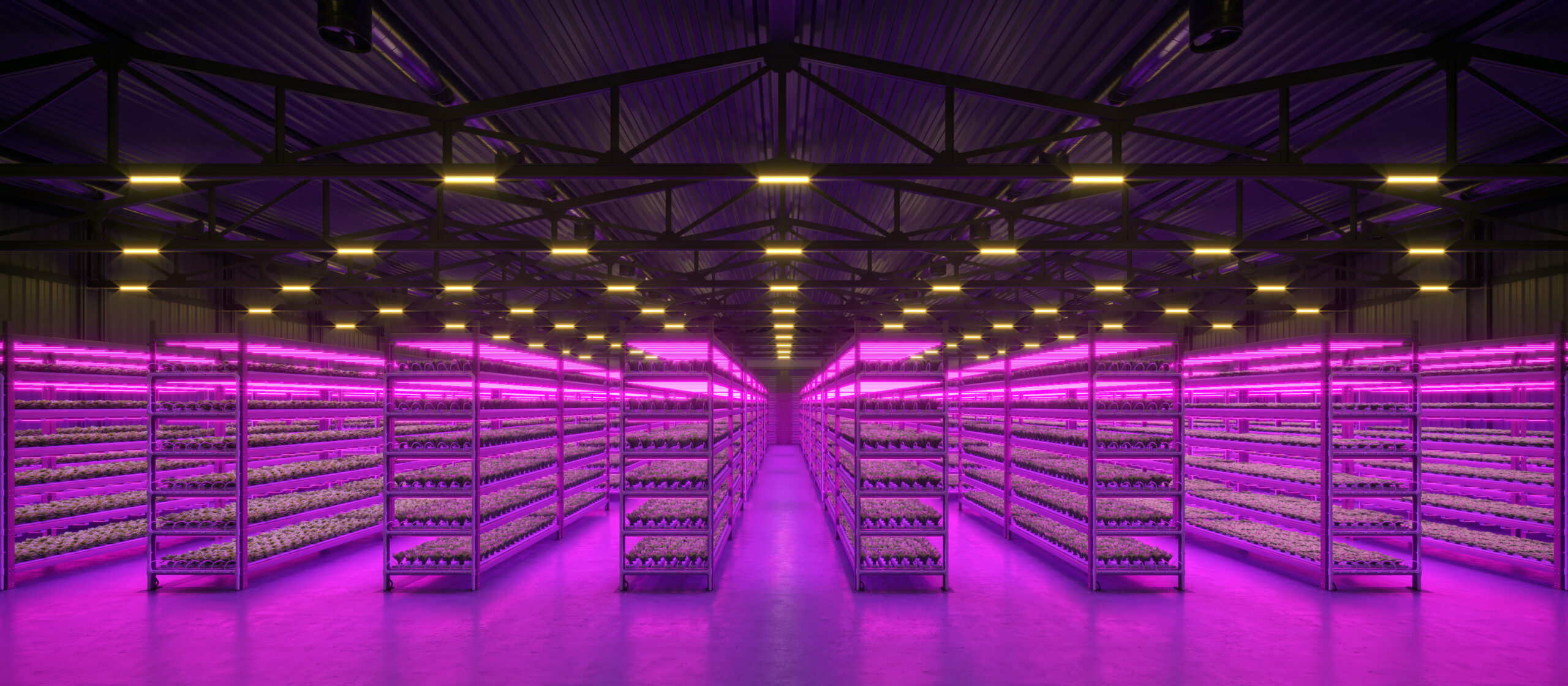
Vertical farming is an innovative approach to growing crops that involves stacking layers of plants in an indoor environment. By using LED lighting and advanced technology, vertical farming optimizes resources, reduces the carbon footprint of agriculture, and provides a sustainable solution to food production.

BENEFITS OF VERTICAL FARMING
RESOURCE OPTIMISATION
Vertical farming optimizes the use of resources such as water and energy by making use of indoor space and advanced technologies. This reduces the need for large amounts of land and water required for traditional agriculture.
EFFICIENT USE OF SPACE
Vertical farming allows for high-density crop production in small spaces, making it an ideal solution for urban areas where land is scarce.
REDUCED ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT
Indoor farming protects crops from pests and diseases, reducing the need for harmful chemicals. Water usage can be optimized, with up to 70% less water required than traditional farming methods, reducing the strain on water resources and mitigating the effects of drought and climate change. Reduced transportation requirements of vertical farms result in fewer carbon emissions from food transport, reducing the carbon footprint of food production.
YEAR-ROUND CROP PRODUCTION
Vertical farming allows for year-round crop production regardless of the season or weather conditions.
SOCIAL BENEFITS
Urban areas with limited access to fresh produce can benefit from local vertical farms, providing a sustainable source of fresh, healthy food. Vertical farms can help promote sustainable development, supporting local communities and reducing the strain on global food systems.
BENEFITS OF LED LIGHTING IN VERTICAL FARMING
ENERGY EFFICIENCY
LED lighting emits less heat and uses less electricity than traditional lighting sources, resulting in lower operating costs and reduced carbon emissions. Low heat emission reduces the need for cooling systems, further reducing energy consumption.
CUSTOMISABLE LIGHTING CONDITIONS
LED lights can be tuned to specific wavelengths and colour spectrums, promoting different aspects of plant growth such as leafy green production, flowering, and fruiting. Farmers can customize the lighting conditions to suit the specific needs of each crop, resulting in higher yields and better-quality produce. LED lights can be programmed to provide the necessary light intensity and duration for different stages of plant growth, resulting in faster and more efficient crop production.
IN CONCLUSION
In conclusion, vertical farming with LED lighting is a sustainable and socially responsible option for food production. Its potential to address food security, reduce the carbon footprint of agriculture, and promote sustainable development makes it an important component of the future of food production. With the continued development of advanced technologies, vertical farming with LED lighting is set to become an increasingly important component of the future of food production.